Encoding
Summary
Encoding is the process of turning discrete data in numeric data. This is useful for certain datasets to be put through machine learning models since most machine learning models cannot interpret discrete data.
Related Sections
One Hot Encoding
One hot encoding is a method of encoding where you split a column into the number of possibilities, and encode each possibility as a 1 for a row of data.
This is practical for a small dataset, but is far too tedious for a large dataset.

Label Encoding
This is a form of encoding where you change each possibility in a column to a certain arbitrary numerical value, usually starting from 0. This allows models to be created using most machine learning models, however the models may think the numbers mean something and form incorrect opinions.
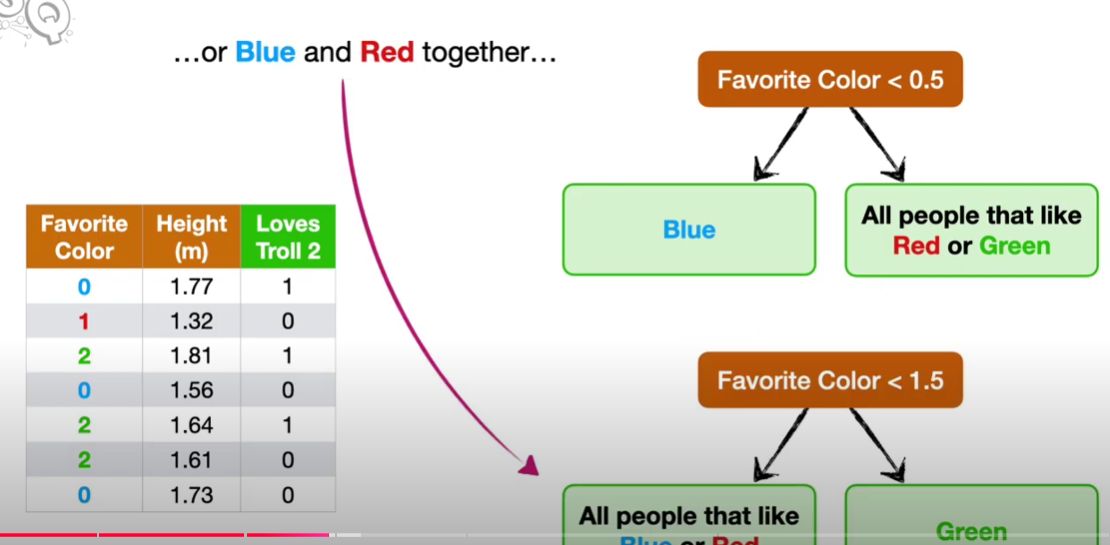
Target Encoding
Target encoding is a method of encoding your discrete variable based on the value you are trying to predict, often using the mean or weighted mean of the target in relation to the possibility.
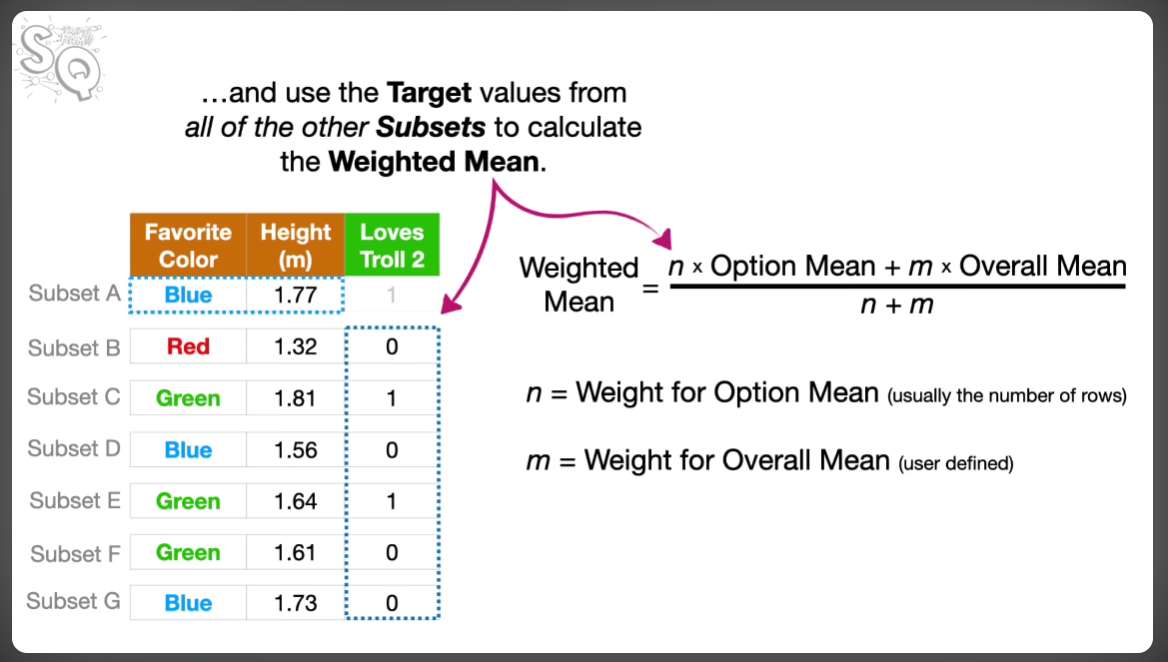
This method is often used in conjunction with a weighted mean method in order to weight the encoded variable with both the current data set and the mean of the target value. This is done to more encode categories we do not have much data on. This method is called Bayesian Target Encoding.
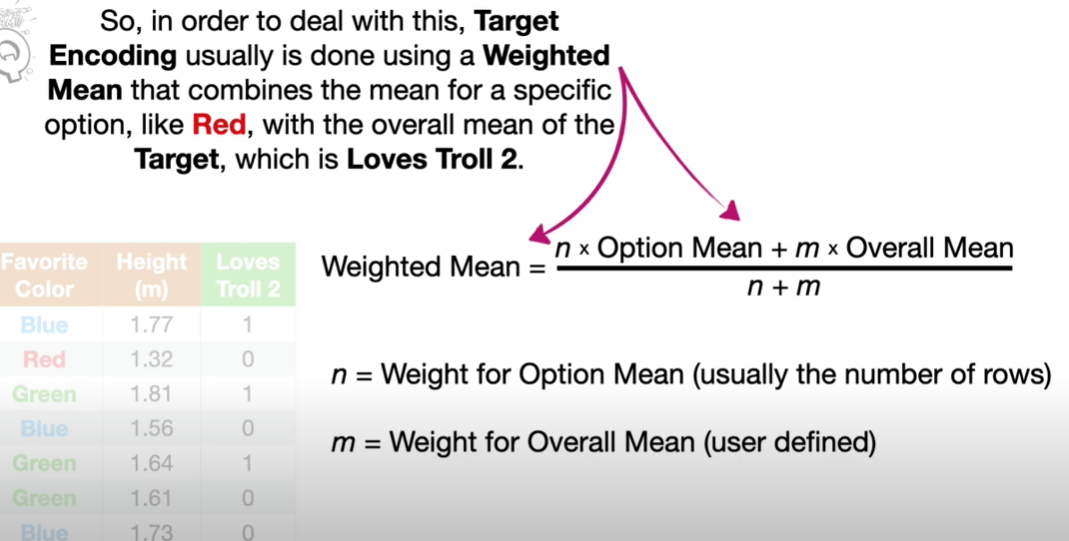
However, this method involves using the target 'loves trolls 2' to set the feature 'Favourite colour'. This is called data leakage and results in overfitting models. The concept of overfitting is explained in Bias vs Variance.
K Fold Target Encoding
K fold target encoding is a method of Bayesian target encoding used however slightly adjusted to avoid data leakage.
This method involves splitting the dataset up into different sets. From each set, we can calculate the weighted mean encoded value for each possibility in a feature.
Then we plug the calculated values in to the other dataset. This would mean we are not using any values in its own dataset to set the value of the feature.